Economy



The Ghanaian Economy
The Ghanaian Economy
Ghana is an average natural resource enriched country possessing industrial minerals, hydrocarbons and precious metals. It is an emerging designated digital economy and mixed economy hybridisation and an emerging market. It has an economic plan target known as the “Ghana Vision 2020”. This plan envisions Ghana as the first African country to become adeveloped country between 2020and 2029 and a newly industrialised country between 2030 and 2039. This excludes fellow Group 24 member and Sub-Saharan African country South Africa, which is a newly industrialised country. Ghana’s economy also has ties to the Chinese yuan renminbi along with Ghana’s vast gold reserves. In 2013, the Bank of Ghana began circulating the renminbi throughout Ghanaian state-owned banks and to the Ghana public ashard currency along with the national Ghana cedi for second national trade currency Ghana is the leader in the adoption of digital financial services in Africa and set to increase financial inclusion to more than 85% until 2024 Between 2012 and 2013, 37.9 percent of rural dwellers were experiencing poverty whereas only 10.6 percent of urban dwellers were. Urban areas hold greater opportunity for employment, particularly in informal trade, while nearly all (94 percent) of rural poor households participate in the agricultural sector.
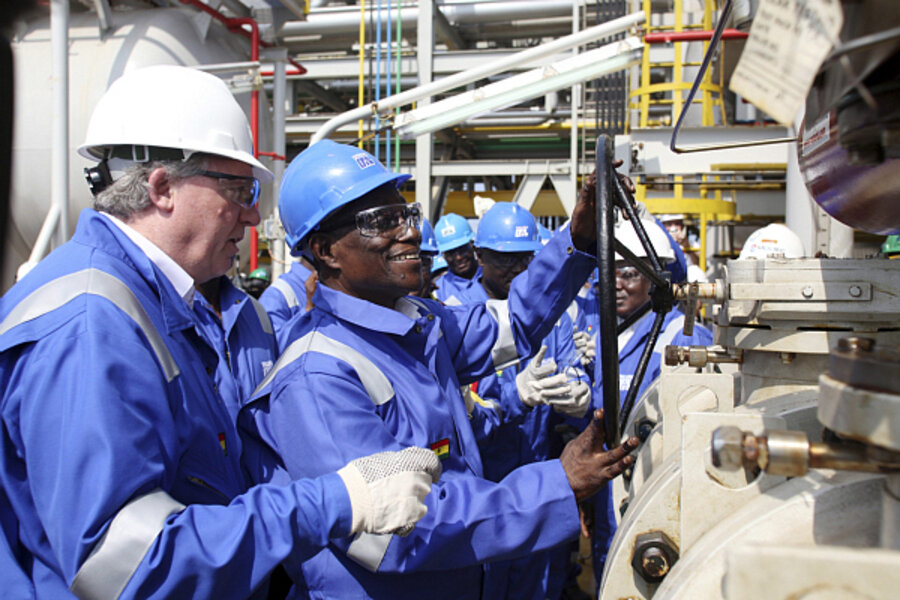
The state-owned Volta River Authority and Ghana National Petroleum Corporation are the two major electricity producers The Akosombo Dam, built on the Volta River in 1965, along with Bui Dam, Kpong Dam, and several other hydroelectric dams provide hydropower. In addition, the Government of Ghana has sought to build the second nuclear power plant in Africa.
The Ghana Stock Exchange is the 5th largest on continental Africa and 3rd largest in sub-saharan Africa with a market capitalisation of GH¢52.7 billion in 2012 with the South AfricaJSE Limited as first. The Ghana Stock Exchange (GSE) was the 2nd best performing stock exchange in sub-saharan Africa in 2013.
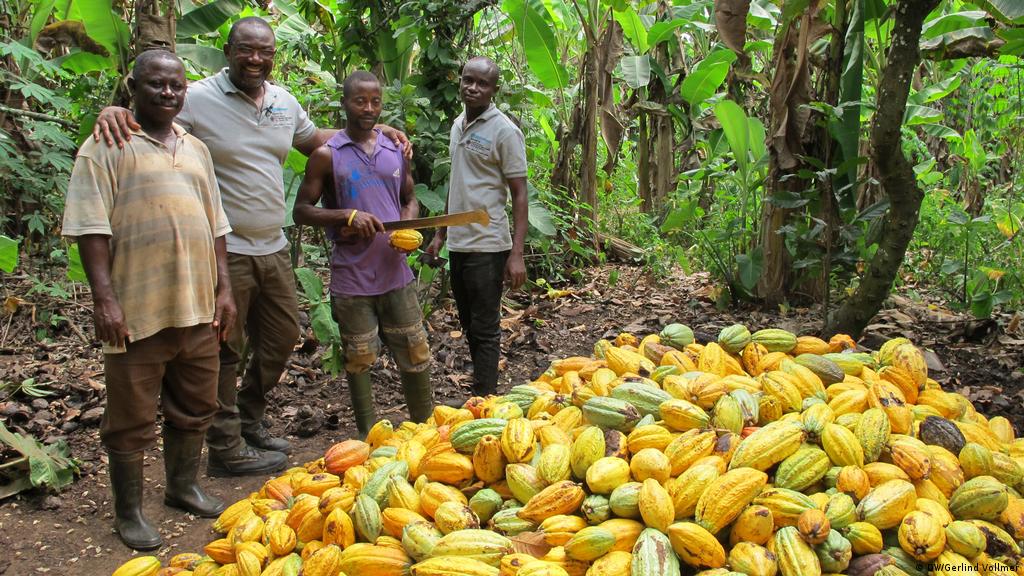
Ghana also produces high-quality cocoa. It is the 2nd largest producer of cocoa globally, and was projected to become the world’s largest producer of cocoa in 2015.
Ghana is classified as a middle income country. Services account for 50% of GDP, followed by manufacturing (24.1%), extractive industries (5%), and taxes (20.9%).
Ghana announced plans to issue government debt by way of social and green bonds in Autumn 2021, making it the first African country to do so. The country, which is planning to borrow up to $5 billion on international markets this year, would use the proceeds from these sustainable bonds to refinance debt used for social and environmental projects and pay for educational or health. Only a few other nations have sold them so far, including Chile and Ecuador. The country will use the proceeds to forge ahead with a free secondary-school initiative started in 2017 among other programs, despite having recorded its lowest economic growth rate in 37 years in 2020